- Alert box
- Confirm box
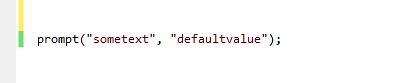
- Prompt box
An alert box is often used if you want to make sure information comes through to the user. When an alert box pops up, the user will have to click "OK" to proceed. Syntax of Alert Box is as follows :


A confirm box is often used if you want the user to verify or accept something. When a confirm box pops up, the user will have to click either "OK" or "Cancel" to proceed. If the user clicks "OK", the box returns true. If the user clicks "Cancel", the box returns false. Syntax of Confirm Box is as follows :


A prompt box is often used if you want the user to input a value before entering a page. When a prompt box pops up, the user will have to click either "OK" or "Cancel" to proceed after entering an input value. If the user clicks "OK" the box returns the input value. If the user clicks "Cancel" the box returns null. Syntax of Prompt Box is as follows :